While it’s not totally necessary to know all about blockchain technology to invest in crypto. It’s quite helpful to have a basic knowledge as it’s the cornerstone of all crypto currencies.

A blockchain is a type of database which stores a list of transactions or other data in blocks, which are “chained” together in chronological order.
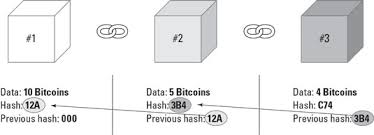
Each block has a finite size and when the newest block is full it is “chained” to the previous one.
Each block is given a timestamp when added to the blockchain and once added it cannot be changed.
Cryptographic Hash
This “chain” that links the blocks together consists of a cryptographic hash, which is a long alpha numeric code. It can be thought of as the blocks fingerprint, which is unique to each block. Each block contains its own hash and the hash of the previous block, hence creating a chain. These cryptographic hashes are why most block chains are referred to as cryptos or crypto currencies.
These hashes are created based on the information within the block. If someone tampers with a n older block and changes the information within, the hash will change. Therefore, the next block will become invalid as it no longer stores the correct hash of the previous block, so the chain will be broken.
Decentralised Ledger
To keep blockchains secure they are used as a decentralised ledger. This is where there is a network of hundreds or thousands of people with a complete copy of the blockchain (called nodes). When a new block is created it is sent to all nodes, who check it is valid and then add it to the end of the blockchain. This is known as consensus. If a block is found to be invalid it will be rejected.
This makes blockchains very secure as there are thousands of identical copies spread far and wide. To tamper/change a block you would have to change it on 51% of all nodes. The computing power required to do this makes it virtually impossible.
Proof-of-Work
This creates trust in the data. Before a block can be added to the chain a few things must happen:
- First a cryptographic puzzle must be solved thus creating the block.
- The computer that solves the puzzle first shares the solution to all the other computers on the network. This is called proof-of-work.
- The network will then verify this proof-of-work and if correct, the block will be added to the chain.
Here’s a great clip to explain blockchains visually: Youtube.com/watch?v=3xGLc-zz9cA
Smart Contracts
Another feature of blockchains are smart contracts. These contracts are simple programs stored on the blockchain. They automatically perform an action when certain conditions are met. E.g. IF x DO y, ELSE DO z. These are very powerful and can operate without human intervention. I might expand on smart contracts in a future post.
While most of us know Satoshi Nakamoto was the person/group that created bitcoin. We often overlook the fact that while creating bitcoin he/they also created the first successful implementations of blockchains, decentralised ledgers and proof of work. While others came up with the concepts it was Satoshi that successfully put them to use.
This post may have been heavy going for some, but i thought it was important to cover some of the concepts behind crypto. Now we can get on with the fun part. Setting up your own wallet and buying some crypto! Stay tuned.

